Oracle Designs in Web3
This page provides backgrond information on some of the most prevalent consensus-based oracles for price feed data, including Chainlink, Pyth, and the Nibiru Oracle Mechanism.
Related Oracle Pages
- Nibiru Oracle (EVM) - Usage Guide
- Integrating with Oracles on Nibiru
- Using the Band Protocol Oracle on Nibiru
Nibiru Oracle Module
The Nibiru Oracle module connects the Nibiru blockchain to external data sources, which is essential for decentralized finance (DeFi). It works by having validator nodes act as oracles, collectively voting on exchange rates for various crypto asset pairs.
This decentralized approach aims to prevent manipulation and single points of failure by aligning incentives between validators and traders, making potential attacks more costly and difficult. The process involves validators submitting price proposals, with the system calculating a weighted median to establish the official on-chain exchange rate.
The module features a structured voting cycle (PreVote, VotePeriod, PostVote) for oracles to reach consensus on exchange rates. Technical aspects include slashing mechanisms to penalize inaccurate or non-participating validators and reward systems for those providing accurate data. By comparing oracle inputs against a reference standard, the module ensures data correctness.
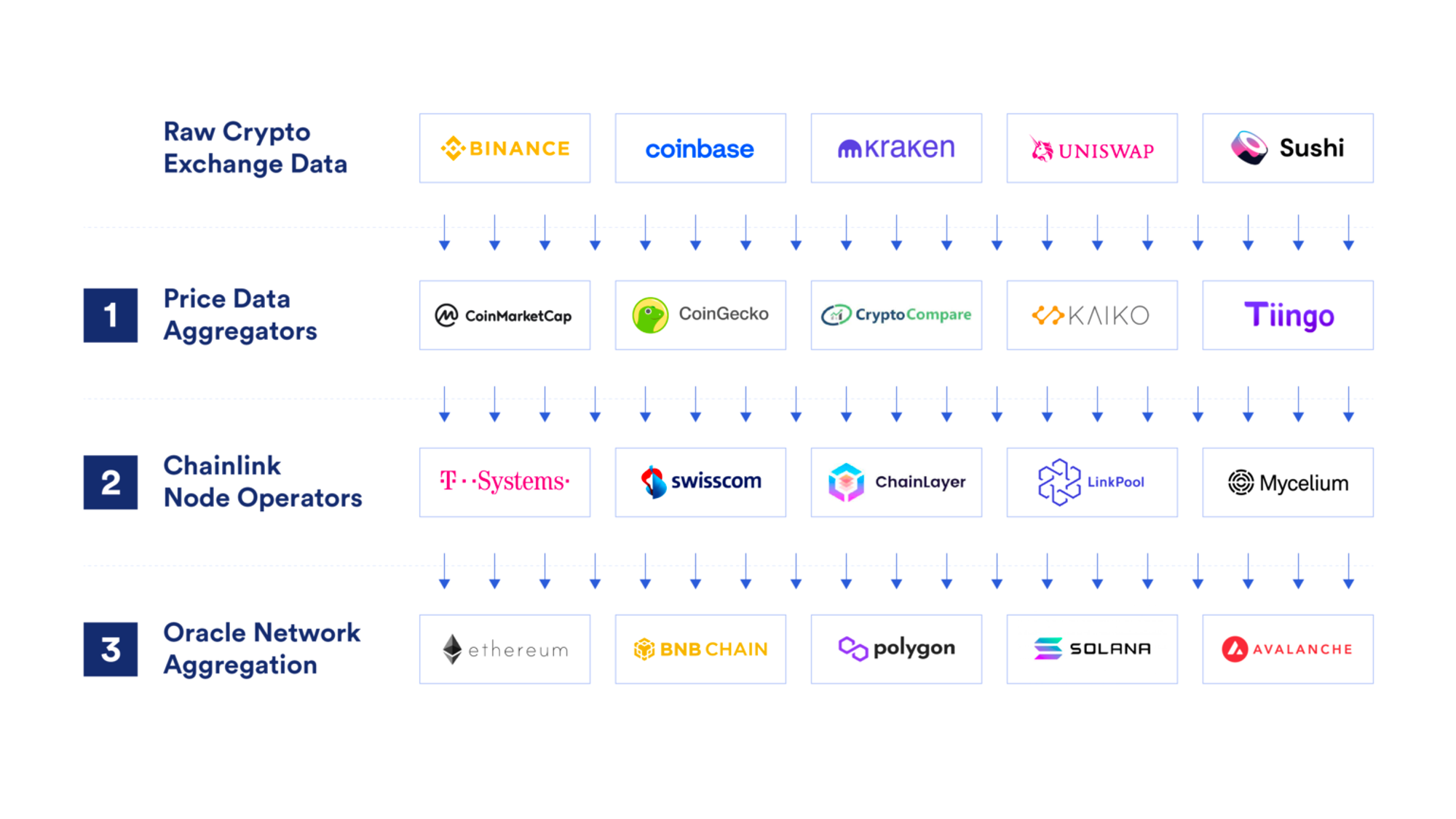
Chainlink
ChainLink relies on a network of independent node operators who are rewarded with LINK tokens in exchange for honest and high-quality performance as oracles. These independent nodes deposit LINK tokens as collateral and are punished for poor performance, whether malicious or not.
A smart contract may request data, which triggers an “event”. Node operators listen for these events and in turn grab the requested off-chain data from a variety of external sources and send it over as a transaction.
The data is first aggregated by the Chainlink Nodes at the data source level. The provided responses are then in turn aggregated at the Node Operator level.
Pyth Oracle
Pyth is focused on financial market data and partners with over 70 established firms, including large exchanges and market making firms. By connecting directly to their API, they’re able to quickly provide prices for commodities, US equities, and cryptocurrencies.
Data publishers include Jump Trading Group, Chicago Trading Company, Jane Street, and many more. These data publishers stake PYTH tokens as collateral to incentivize good behavior, and are rewarded for providing timely and reliable data. Those relying on the data may elect to pay small fees in order to gain protection from oracle failures.
MakerDAO
MakerDAO is the largest DeFi protocol and enables collateral loans in the form of their decentralized stablecoin DAI. They use a price feed oracle to determine the prices of the posted collateral, in order to trigger liquidations when appropriate.
Price feeds are collected by individuals operating pseudonymously, as well as organizations who operate with public identities. Example organizations include well-known DeFi entities such as dYdX, 0x, and Gnosis. Those providing these price fees are voted on by MKR token holders, and these prices are inputted into what’s known as the Oracle Security Module (OSM). The OSM delays prices by an hour in order to freeze an oracle in the event of any issue or compromise.