Nibiru Architecture
The technical architecture of Nibiru consists of an execution engine and a consensus engine. The execution engine is what computes new state updates given some transactions, while the consensus engine validates and handles the gossiping of blocks, ultimately adding them to the chain.
Execution Engine
The execution engine of Nibiru is the overarching component that implements business logic and manages the "state" that makes Nibiru a state machine. This is where transactions are processed and disseminated.
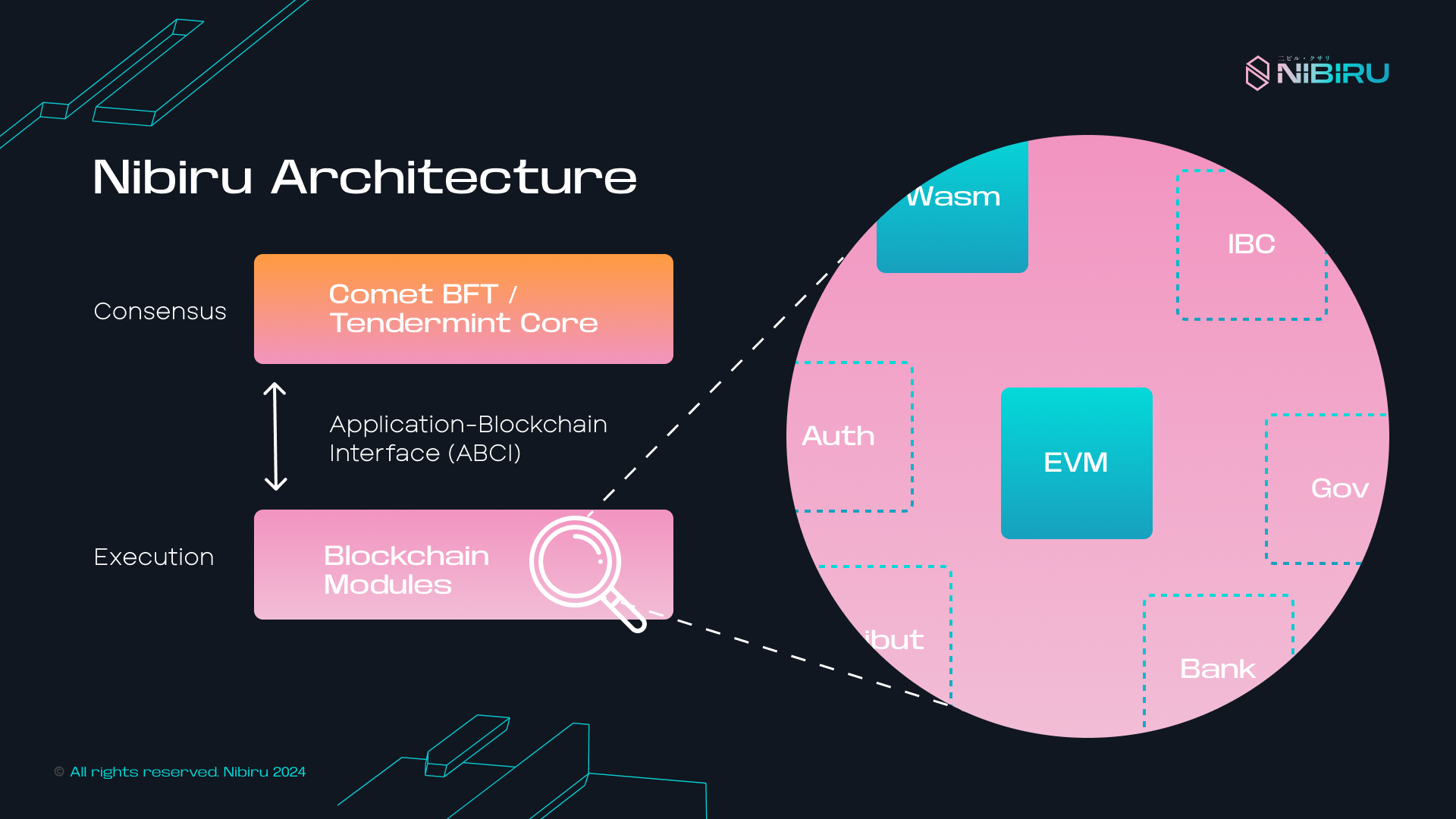
This piece of the architecture includes the Nibiru EVM and Wasm execution environments for smart contracts and other custom "modules".
NibiruBFT Consensus Engine
Nibiru uses NibiruBFT, an evolution on CometBFT, as its consensus algorithm. In blockchain networks, the consensus engine is responsible for block building, the gossip of blocks on the peer-to-peer (P2P) network, and management of consensus for new blocks to be added to the chain.
Block
A block is an ordered sequence of transactions along with a cryptographic hash that references the prior, or parent, block that came before. A block's hash is derived from the data and resulting state of executing the state transitions (transactions) it contains.
Appendix: Module Reference
Modules — Nibiru
| Module | Active? | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EVM | ✔️ | Implements Nibiru EVM, which manages an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) state database and enables the execution of Ethereum smart contracts. Nibiru EVM is an extension of "geth" along with "web3" and "eth" JSON-RPC methods. |
| Wasm | ✔️ | Handles Wasm smart contracts. This is the interface with the Wasm VM. |
| Dev Gas | ✔️ | Implements a Smart contract gas royalties mechanism allowing builders to capture the value they create. |
| Epochs | ✔️ | Often in the SDK, we would like to run certain code every so often. The purpose of epochs module is to allow other modules to set that they would like to be signaled at regular intervals. So another module can specify it wants to execute code once a week, starting at UTC-time = x. epochs creates a generalized epoch interface to other modules so that they can easily be signaled upon such events. |
| Oracle | ✔️ | Handles the decentralized oracle module. |
| Common | ✔️ | Holds helper and utility functions to be utilized by other x/ cosmos-sdk modules. |
| Common/testutil | ✔️ | Helper functions for unit and integration tests. |
Modules — Cosmos-SDK
Production-grade modules imported from the Cosmos-SDK:
| Module | Active? | Description |
|---|---|---|
| auth | ✔️ | Authentication of accounts and transactions for Cosmos SDK application. |
| authz | ✔️ | Authorization for accounts to perform actions on behalf of other accounts. |
| bank | ✔️ | Token transfer functionalities. |
| base | ✔️ | |
| capability | ✔️ | Object capability implementation. |
| crisis | ✔️ | Halting the blockchain under certain circumstances (e.g. if an invariant is broken). |
| crypto | ✔️ | |
| distribution | ✔️ | Fee distribution, and staking token provision distribution. |
| evidence | ✔️ | Evidence handling for double signing, misbehaviour, etc. |
| feegrant | ✔️ | |
| genutil | ✔️ | |
| gov | ✔️ | On-chain proposals and voting. |
| mint | ✔️ | Creation of tokens native to the chain. |
| params | ✔️ | Globally available parameter store. |
| slashing | ✔️ | Validator punishment mechanisms. |
| staking | ✔️ | Proof-of-Stake layer for public blockchains. |
| tx | ✔️ | |
| upgrade | ✔️ | Software upgrades handling and coordination. |
| vesting | ✔️ |
Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC)
The IBC module has its own repository, ibc-go.